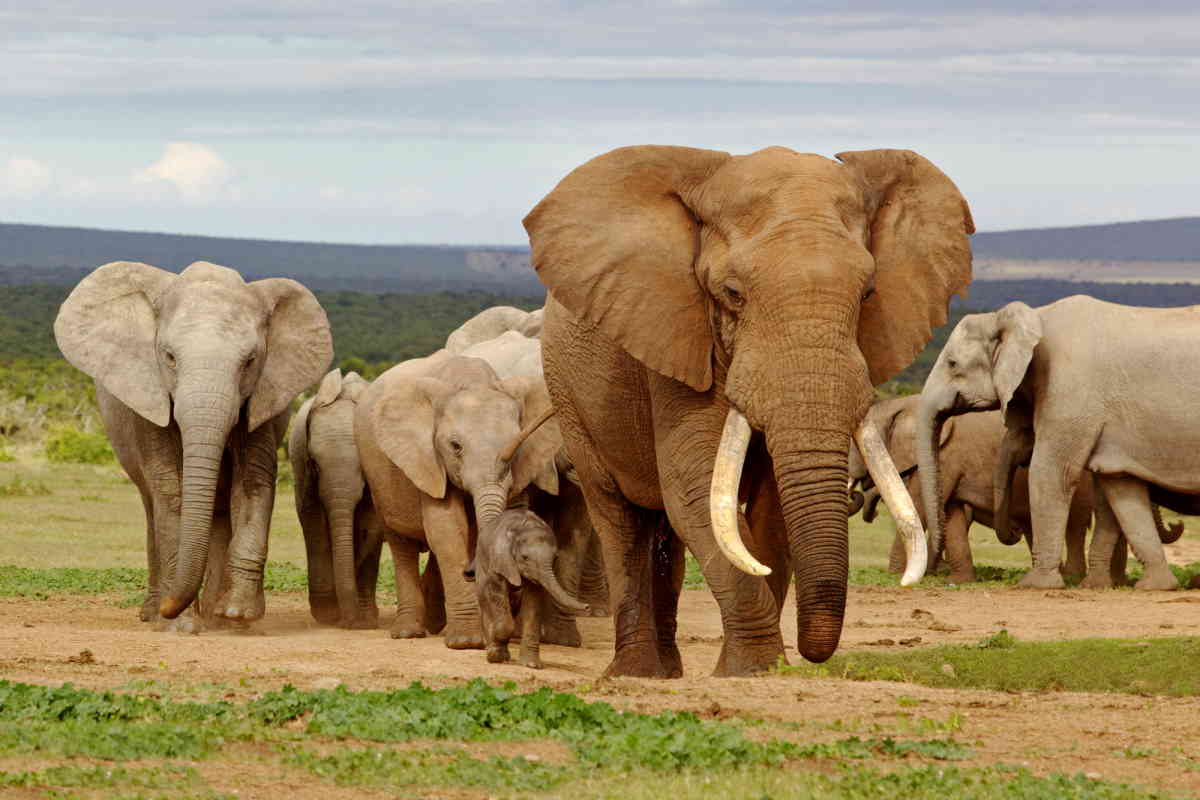
Have you ever wondered how many elephants are left in the world, as of 2025? Elephants are wonderful creatures for many reasons! They are intelligent and social animals that form close bonds with one another and live in complex family groups. They are also highly adaptable and can survive in a variety of different habitats, from the savannas of Africa to the rainforests of Asia.
In addition, they play important roles in their ecosystems as keystone species, meaning that their presence can have a significant impact on the overall health and balance of their habitats. Finally, elephants have unique and fascinating biology, including their large size, long lifespan, and remarkable memory.