What is the biggest star in the Universe? In fact, it is really hard to give an exact answer to this question since the universe is big, neighboring and the other galaxies are billions of light-years away from us. But, we can give it a try. Here are the top 7 biggest stars in the universe currently known by radius.
Since the Sun is the best-known star for us, solar radius and solar mass are two useful units of measurement to depict how big is a star. A solar radius is approximately 690,000 km (432,000 miles) and 1 solar mass is 2 x 1030 kilograms (4.3 x 1030 pounds).
Please keep in mind that the list below can change at any time with new findings and discoveries.
Biggest stars in the Universe (as far as we know so far)
7. VY Canis Majoris: 1,420 ± 120 Solar Radii
One of the largest known stars, and also one of the most luminous and massive red supergiants (or red hypergiants), VY Canis Majoris has a radius of 1,420 ± 120 solar radii. This red hypergiant star was previously estimated to be 1,800 to 2,200 solar radii, making it even larger than the orbit of Saturn (which is between 1,940-2,169 solar radii), but that size put it outside the bounds of stellar evolutionary theory. New measurements brought it down to size.
But, still, if placed at the center of the Solar System, this red hypergiant’s surface would extend beyond the orbit of Jupiter, which is between 1,064 and 1,173 solar radii. It is big, really big: you can see how far away is Jupiter from the Sun using a scaled model of our solar system.
It is located 1.2 kiloparsecs (3,900 light-years) away from Earth in the constellation of Canis Major. Some sources still list VY Canis Majoris
6. HD 143183: 1,480-1,830 Solar Radii
HD 143183 is a red supergiant or hypergiant star in the constellation Norma, at a distance of over 2 kiloparsecs (over 6,523 light-years). It is one of the most luminous red supergiants and its calculated radius is between 1,480 and 1,830 solar radii.

5. Westerlund 1-26: 1,530-1,580 Solar Radii
With a radius between 1,530-2,550 solar radii, Westerlund 1-26 is one of the largest stars discovered so far. This red supergiant or hypergiant is located on the outskirts of the Westerlund 1 super star cluster, a compact young super star cluster in the Milky Way galaxy, about 3.5-5 kiloparsecs (11,415-16,300 light-years) away from Earth. Westerlund 1-26 is located about 11,500 light-years from
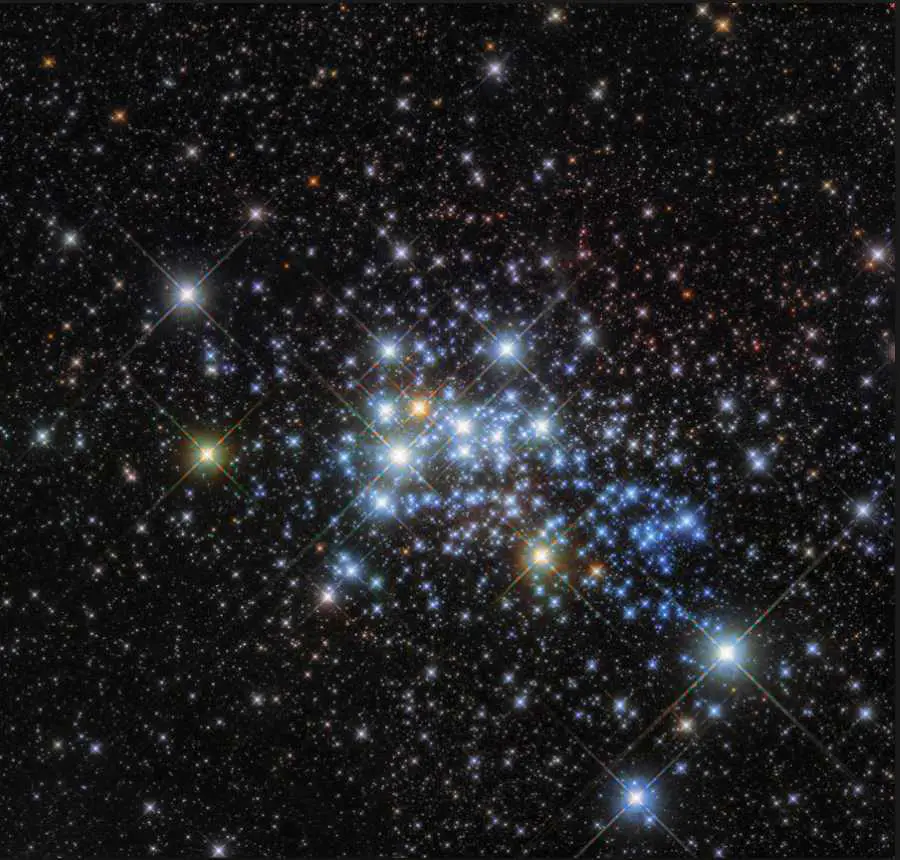

Most of Westerlund 1’s stars are thought to have formed in the same burst of activity, meaning that they have similar ages and compositions. The cluster is relatively young in astronomical terms – at around three million years old it is a baby compared to our own Sun, which is some 4.6 billion years old.
4. RW Cephei: 1,535 Solar Radii
Estimated at 1,535 solar radii, RW Cephei is an orange hypergiant star in the constellation Cepheus. It is about 4 kiloparsecs (14,000 light-years) away from Earth.

3. WOH G64: 1,540-1,730 Solar Radii
163,000 light-years away from Earth and one of the largest known stars, with a radius of 1,540 to 1,730 solar radii, WOH G64 is a red hypergiant star in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of our Milky Way. Some estimate it is even bigger: in 2004, Monnier et al. calculated that the star has a radius of around 3,000 radii.

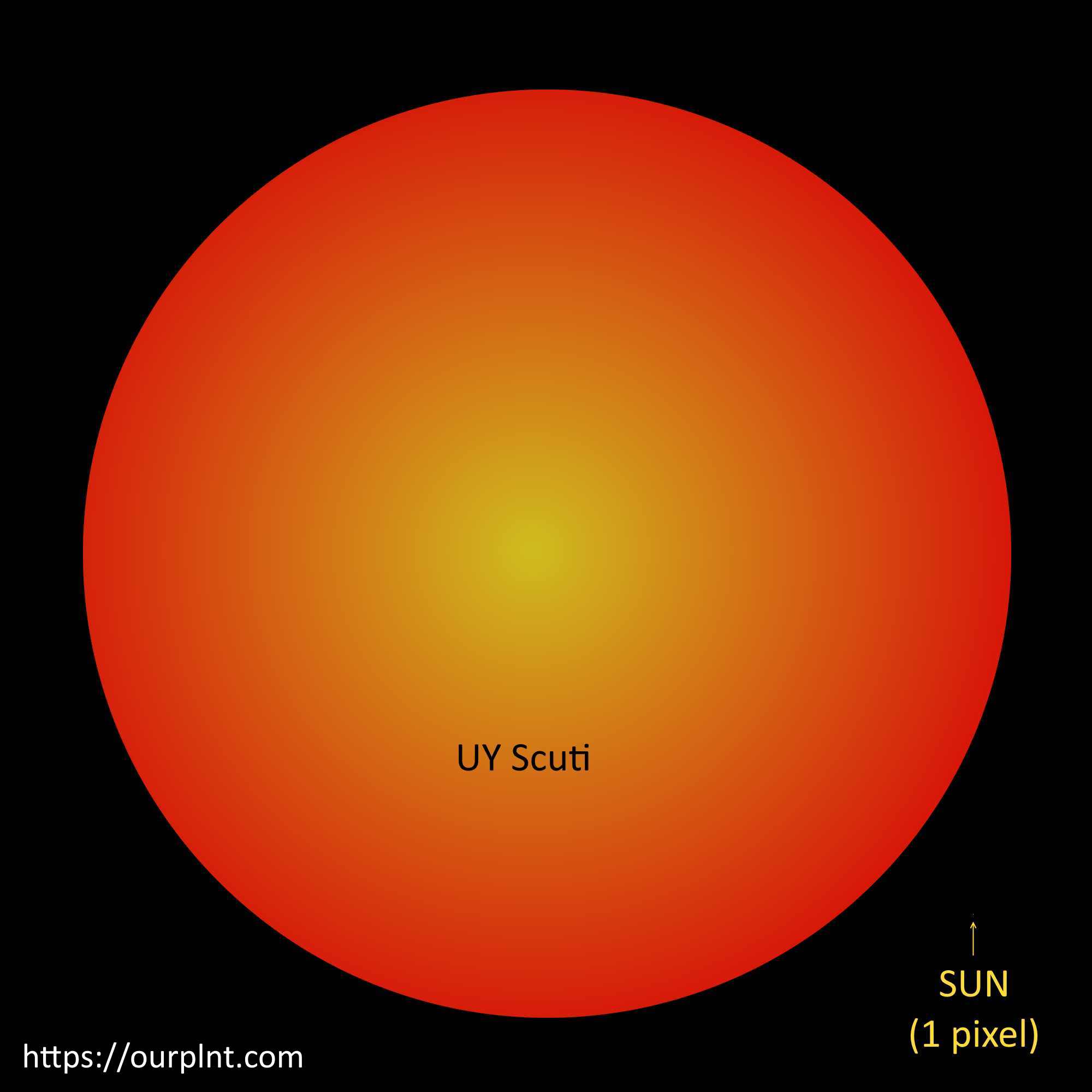
2. UY Scuti: 1,708 ± 192 Solar Radii
With a radius of 1,708 ± 192 Solar Radii, UY Scuti is probably the biggest known star. It was first cataloged in 1860, by German astronomers at the Bonn Observatory.
In the summer of 2012, astronomers using AMBER interferometry from the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in the Atacama Desert in Chile measured the parameters of three red supergiants near the Galactic Center region: UY Scuti, AH Scorpii, and KW Sagittarii. They determined that all three stars are over 1,000 times bigger than the Sun and over 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun. UY Scuti was found to be the largest and the most luminous of the three stars measured, at 1,708 ± 192 R☉ (Solar radii).


1. Stephenson 2-18 (2,150) Solar Radii, the biggest known star in the Universe
The red hypergiant Stephenson 2-18, also known as Stephenson 2 DFK 1 or RSGC2-18 is the largest known star in the Universe. It is so big that around 10 billion Suns could fit inside it.
Stephenson 2-18 is located 20,000 light-years from Earth in the Scutum-Centaurus Arm of the Milky Way galaxy.
What is the most massive star?
UY
UY Scuti has around 10 solar masses.

Sources
- List of Largest Stars on Wikipedia
- VY Canis Majoris on Wikipedia
- HD 143183 on Wikipedia
- Westerlund 1-26 on Wikipedia
- RW Cephei on Wikipedia
- “Mass loss from the M 3 supergiant HD 143183 in a young compact star cluster in Norma”. Astronomy and Astrophysics. 50 (3): 429-434.
- WOH G64 on Wikipedia
- UY Scuti on Wikipedia
- R136a1 on Wikipedia
- What is the Biggest Star in the Universe? by Fraser Cain on Universe Today
- What Is the Biggest Star? on Space.com
- Stephenson 2-18 on Wikipedia
- How Many Elephants are Left in the World in 2025? - August 17, 2025
- Moon Landings: All-Time List [1966-2025] - February 2, 2025
- What Is Max-Q and Why Is It Important During Rocket Launches? - January 16, 2025
