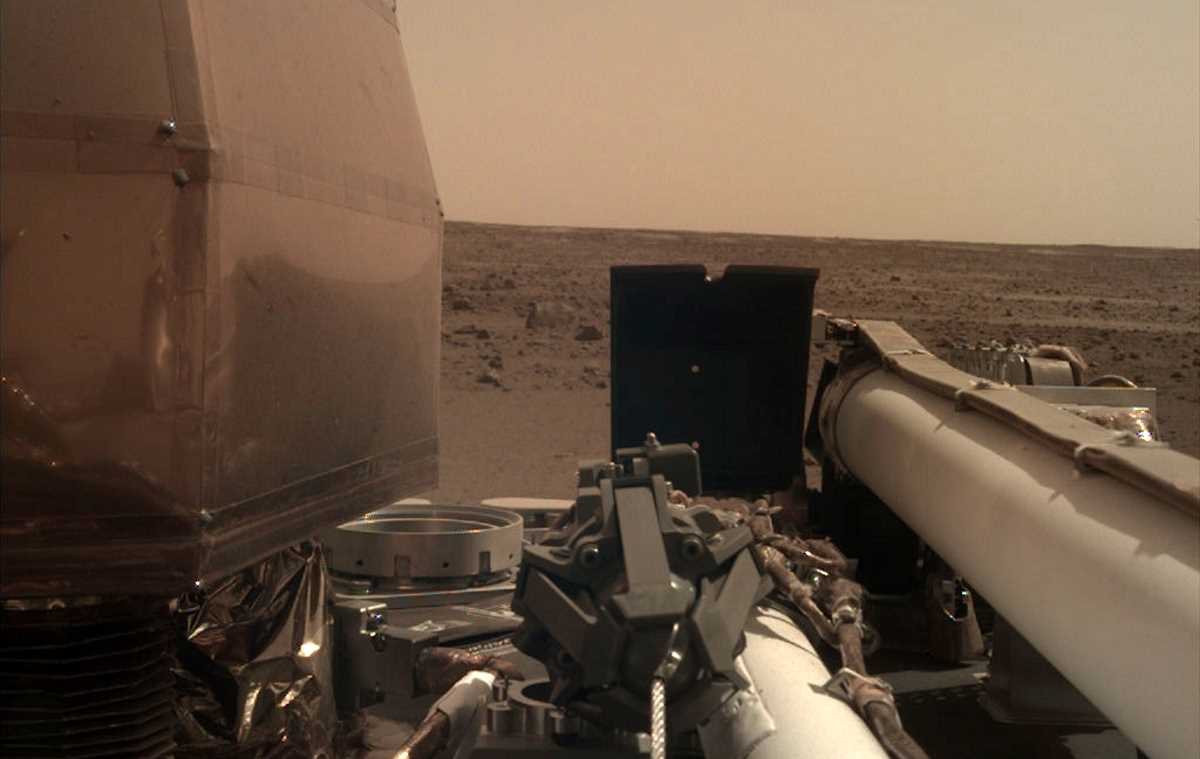
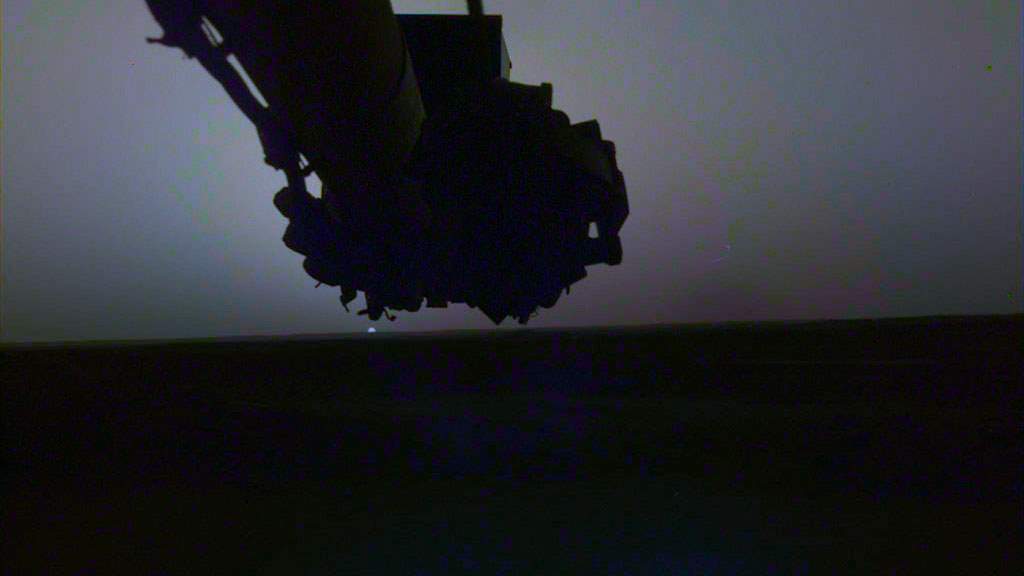
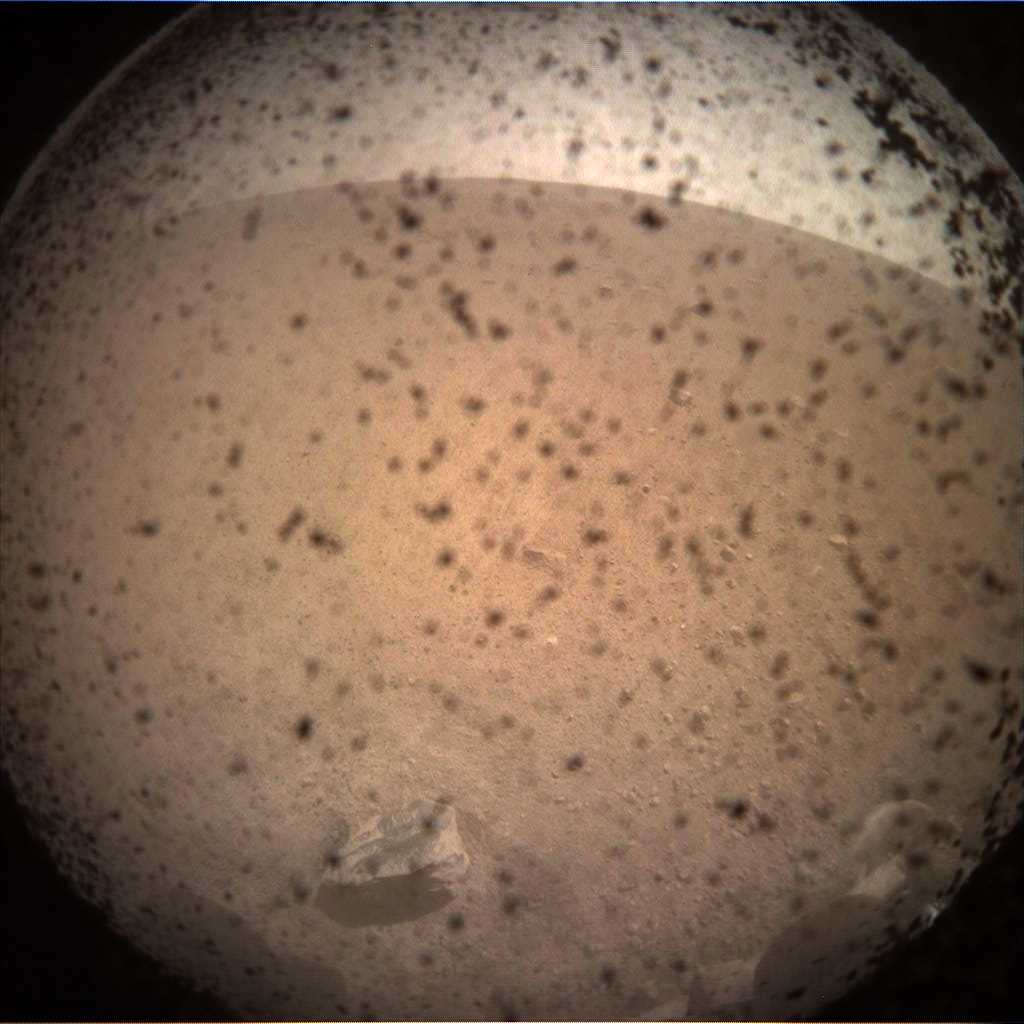
NASA’s InSight Mars Lander (Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy, and Heat Transport – InSight) was launched on 5 May 2018 at 11:05 UTC aboard an Atlas V-401 rocket. It traveled 483 million kilometers (300 million miles) in almost six months and successfully landed at Elysium Planitia on Mars on 26 November 2018 at 19:52:59 UTC. Shortly after landing, it has sent back the first photo. Now, NASA publishes InSight Mission raw images on its website, you can see them any time you want on the mission’s multimedia webpage.
All the published images are in the lossless PNG format. To keep the image sizes low, the images below are in JPG format.


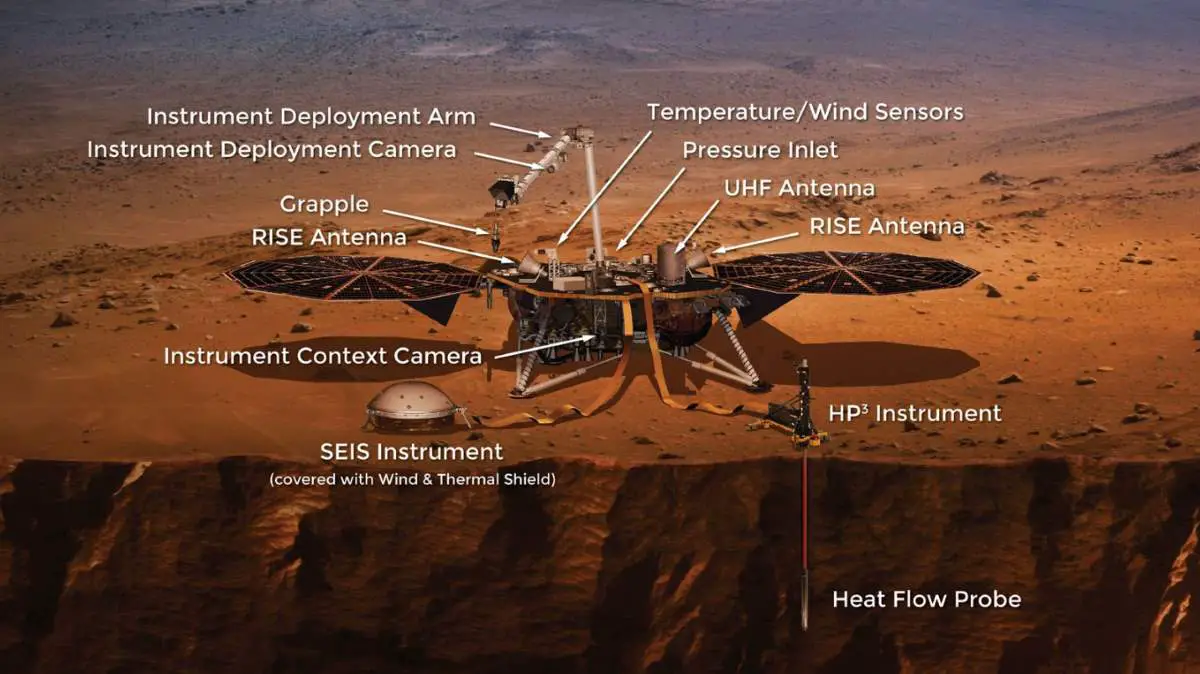
InSight Mars Lander
InSight’s objectives are to place a seismometer, called SEIS, on the surface of Mars to measure seismic activity and provide accurate 3D models of the planet’s interior; and measure internal heat flow using a heat probe called HP3 to study Mars’ early geological evolution. This could bring a new understanding of the processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars – and Earth’s Moon.
NASA’s InSight lander opens a window into the “inner space” of Mars. Its instruments peer deeper than ever into the Martian subsurface, seeking the signatures of the processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner Solar System, more than four billion years ago. InSight’s findings are expected to shed light on the formation of Mars, Earth, and even rocky exoplanets
From the NASA’s Mission Overview page:
Previous missions to Mars have investigated the surface history of the Red Planet by examining features like canyons, volcanoes, rocks,
Because Mars has been less geologically active than the Earth (for example, it does not have plate tectonics), it actually retains a more complete record of its history in its own basic planetary building blocks: its core, mantle and crust.
By studying the size, thickness, density and overall structure of the Red Planet’s core, mantle and crust, as well as the rate at which heat escapes from the planet’s interior, the InSight mission will provide glimpses into the evolutionary processes of all of the rocky planets in the inner solar system.
In terms of fundamental processes that shape planetary formation, Mars is a veritable “Goldilocks” planet, because it is big enough to have undergone the earliest internal heating and differentiation (separation of the crust, mantle, and core) processes that shaped the terrestrial planets (Earth, Venus, Mercury, Moon), but small enough to have retained the signature of those processes over the next four billion years. Within its own structural signature, Mars may contain the most in-depth and accurate record in the solar system of these processes.
What is the purpose of the Insight Mars mission?
NASA’s Robert Frost explains on Quora:
InSight is focused upon the interior structure of Mars. It will use a suite of instruments to examine the interior of Mars and that will help us better understand the formation of rocky planets. Having one data point (Earth) puts a lot of bias in our understanding. Comparing the data we have from Earth’s inner structure with that of Mars can greatly improve our models.
A seismometer called SEIS will document the waves inside the planet and help us understand its structure and its level of tectonic activity.
A heat probe will drill into the surface to study how much heat Mars has stored within it. This will help us understand the composition and evolution of Mars and thus better understand rocky planets, in general.
And two radio antennae will detect the very slight wobbles Mars experiences in its rotation. This will help us understand the uniformity of the planet’s structure and how much of its core is solid or liquid.
The information gained from InSight has the potential to significantly change our understanding of both astronomy and geology. The latter means it could help us better understand how Earth behaves which may improve models for things like earthquake detection and prediction.
And then, above Mars, are the accompanying MarCo cubesats that is a technology testbed. Its success would enable us to produce smaller spacecraft for future exploration and improve communication relays between landers on the surface of a planet and our home receivers on Earth.
Sources
- InSight Mars Lander on NASA.gov
- InSight Mission Overview on NASA.gov
- InSight on Wikipedia
- What is the purpose of the Insight Mars mission? on Quora
- Moon Landings: All-Time List [1966-2025] - February 2, 2025
- What Is Max-Q and Why Is It Important During Rocket Launches? - January 16, 2025
- Top 10 Tallest Rockets Ever Launched [2025 Update] - January 16, 2025


