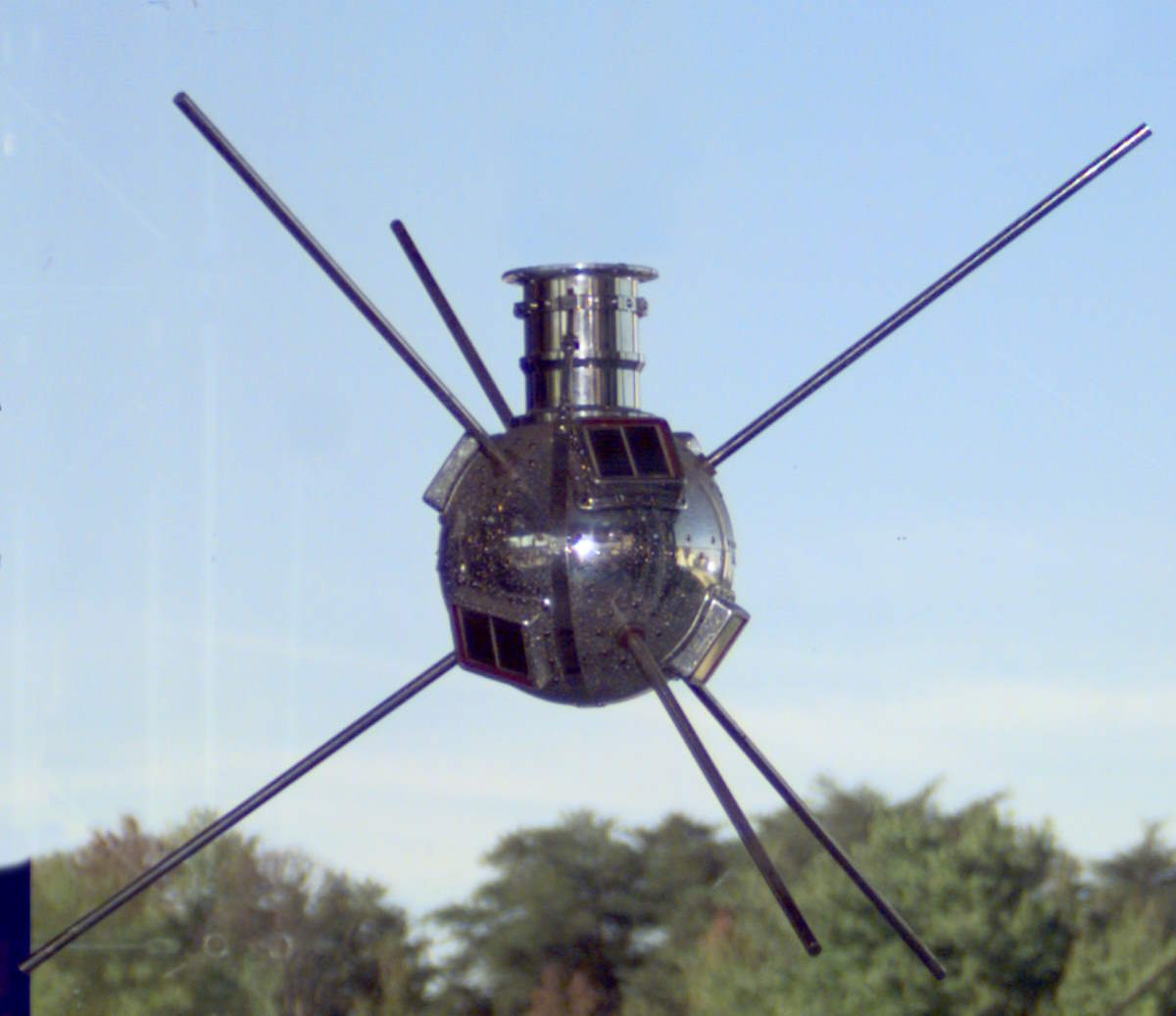
Vanguard 1, launched on March 17, 1958, marks a significant step in space exploration as the first solar-powered satellite. It is also the oldest human-made object still orbiting Earth. The satellite, with a diameter of about 6.4 inches (16.3 cm), demonstrated the viability of solar energy in space missions. While its primary scientific mission has …
Category Archives: This Day in Science, Technology, Astronomy, and Space Exploration History
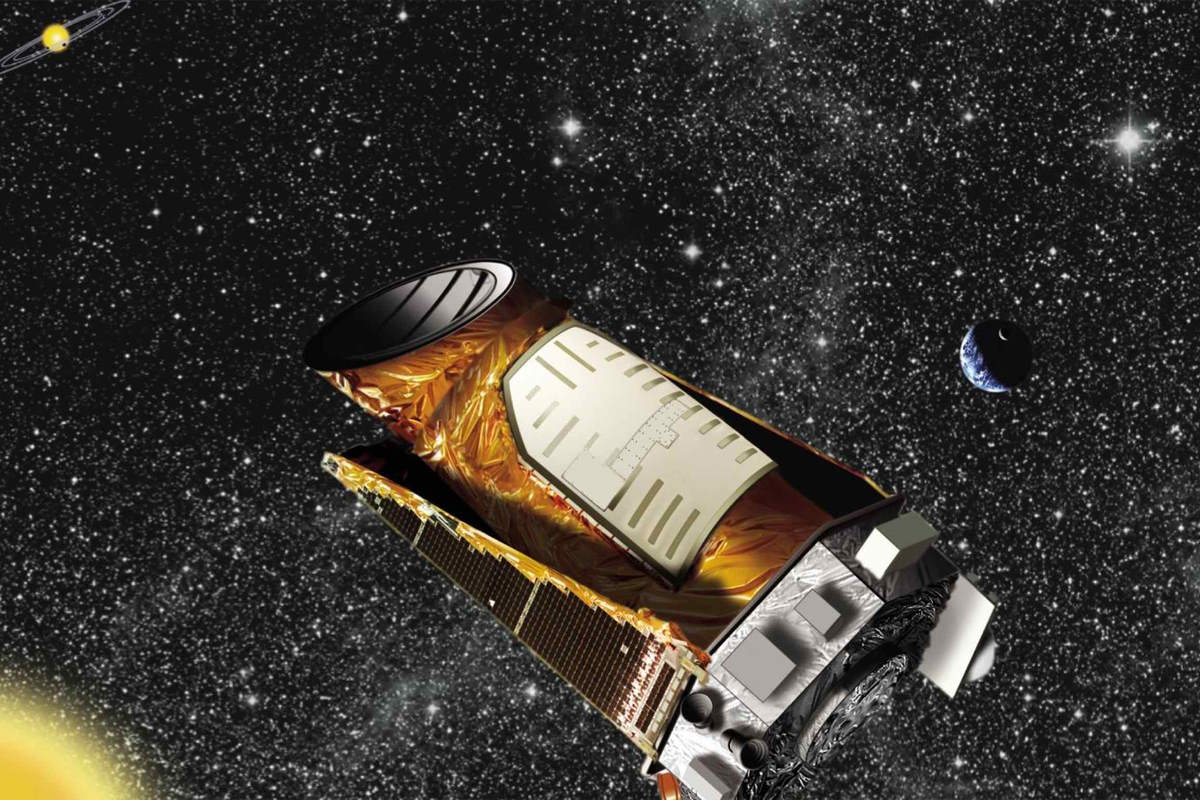
Kepler Space Telescope was launched on March 7, 2009
On March 7, 2009, NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope was launched from Cape Canaveral on top of a Delta II (7925-10L) rocket. It was designed to search for exoplanets – planets orbiting stars outside our solar system. Kepler’s primary mission was to determine how common Earth-like planets are in our galaxy, and it discovered more than …
Continue reading “Kepler Space Telescope was launched on March 7, 2009”
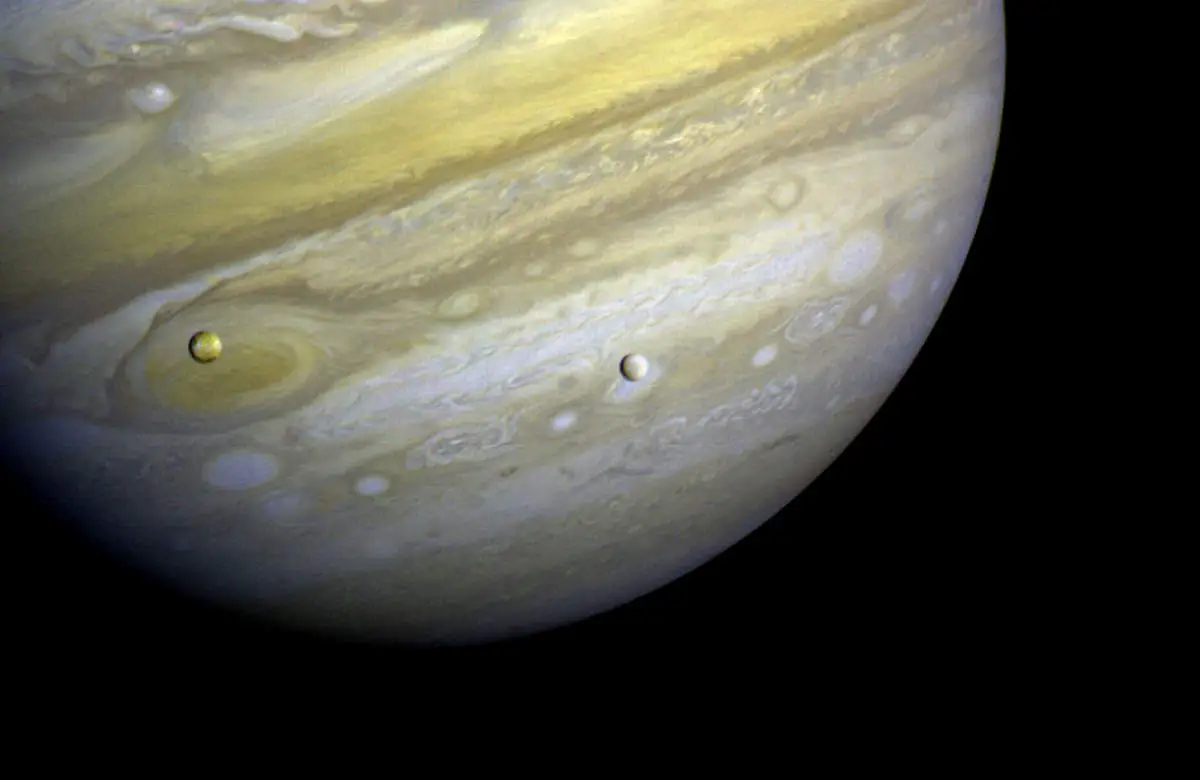
Voyager 1 performed the Jupiter flyby on March 5, 1979
On March 5, 1979, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft performed a Jupiter flyby as it flew within 277,400 kilometers (172,368 miles) of the planet’s cloud tops or 348,890 km/216,790 miles from the center of mass.
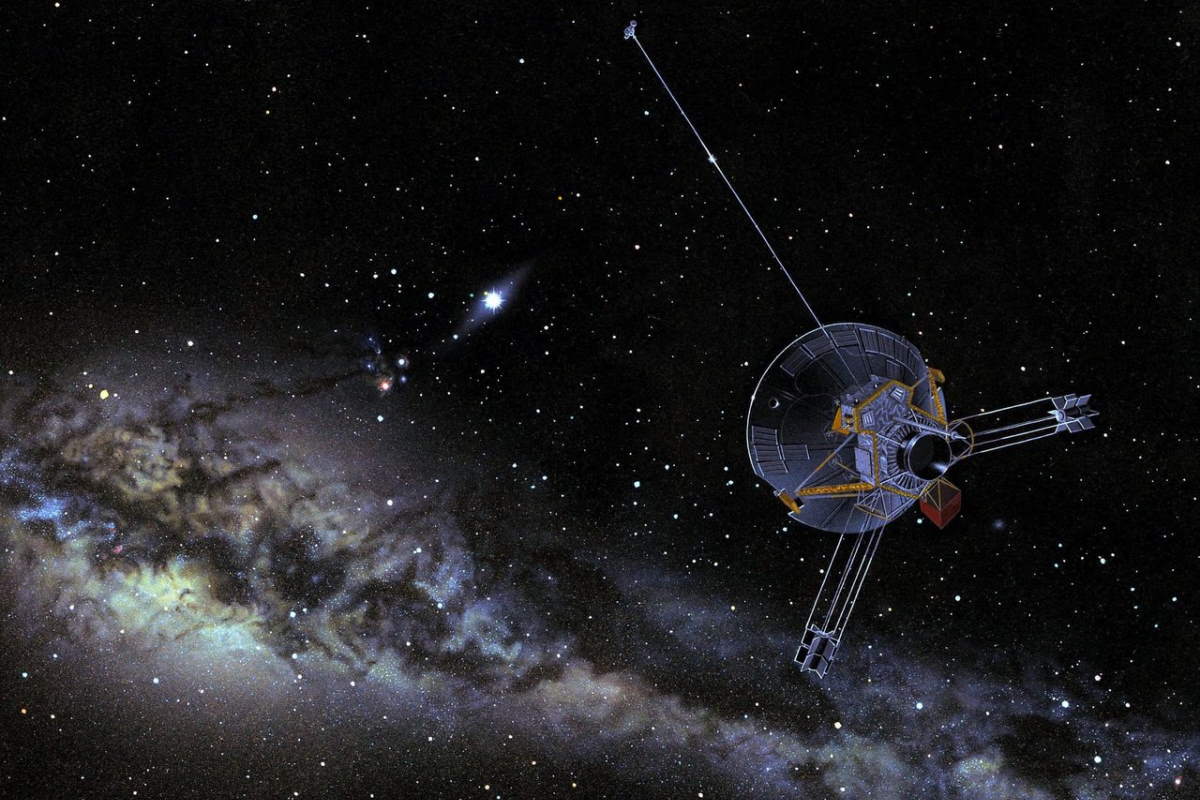
Pioneer 10 was launched on March 2, 1972
On March 2, 1972, Pioneer 10, was launched by NASA on top of an Atlas-Centaur rocket (AC-27 / Atlas 3C no. 5007C / Centaur D-1A) to study Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, and its environment. The mission’s primary goal was to fly by Jupiter and study its atmosphere, magnetosphere, and radiation belts. …
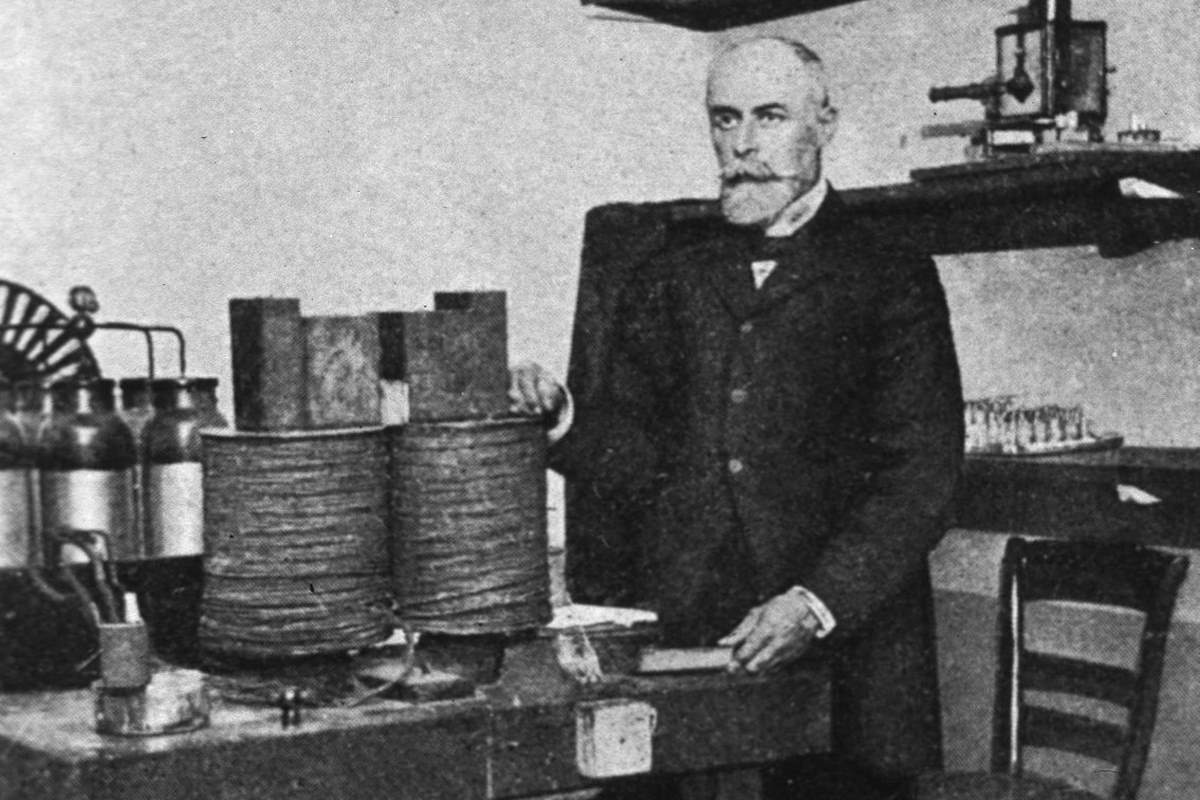
Henri Becquerel accidentally discovered radioactivity on March 1, 1896
On March 1, 1896, French physicist Henri Becquerel (15 December 1852 – 25 August 1908) accidentally discovered radioactivity.
Venera 13 became the first spacecraft to record sounds on another planet [Venus] on March 1, 1982
On March 1, 1982, the landing vehicle of the Soviet Union’s Venera 13 spacecraft landed on Venus and became the first spacecraft to record sounds on another planet.
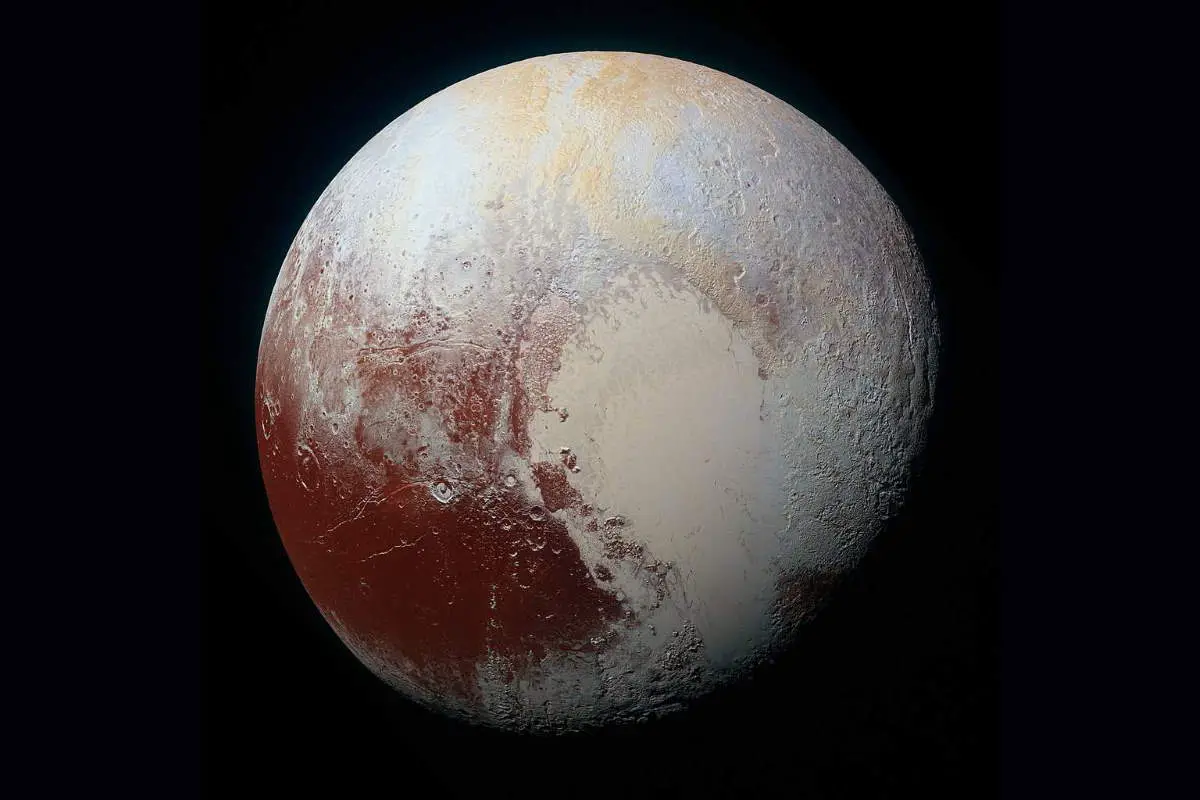
Pluto was discovered on February 18, 1930
Pluto was discovered on February 18, 1930, by the American astronomer Clyde W. Tombaugh (February 4, 1906 – January 17, 1997) at the Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona.
Apollo 1 Tragedy [January 27, 1967]
On January 27, 1967, three NASA astronauts, Roger B. Chaffee (b. February 15, 1935), Virgil I. Grissom (b. April 3, 1926), and Edward H. White II (b. November 14, 1930) died when a flash fire swept through the Apollo 1 command module during a launch rehearsal test. The three men inside perished despite the best …
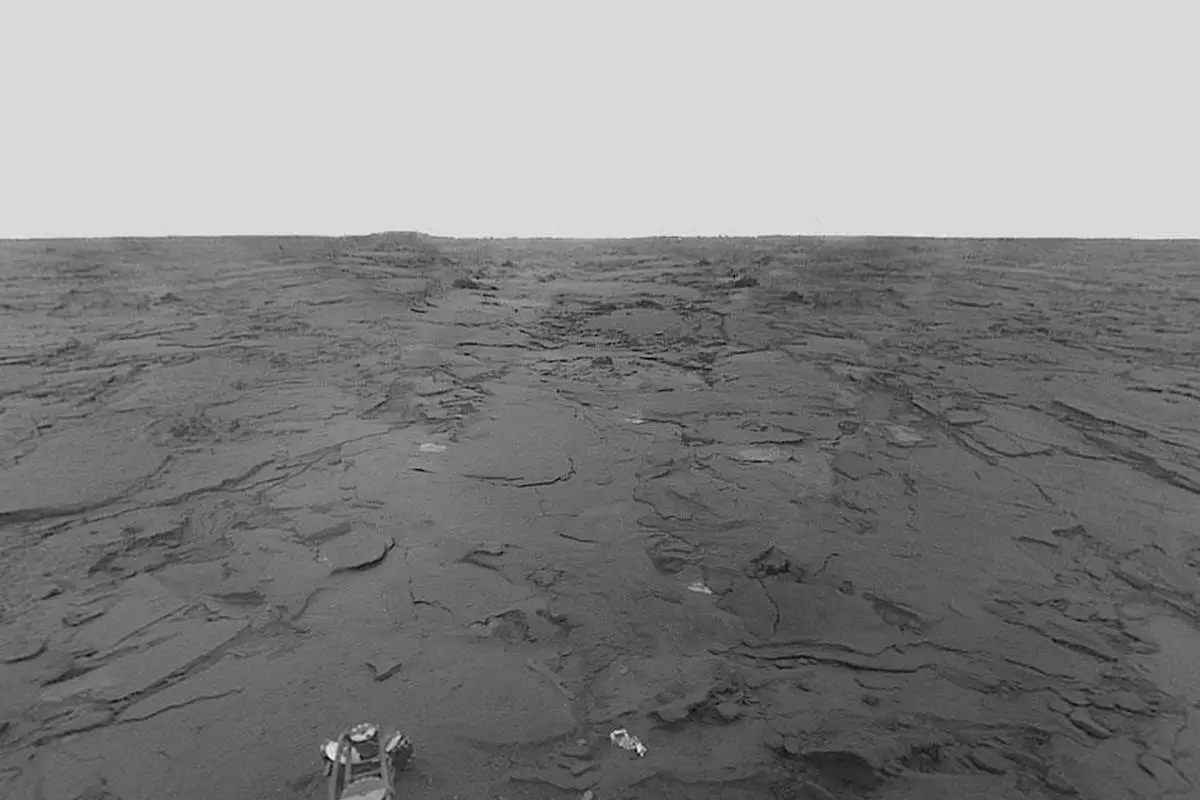
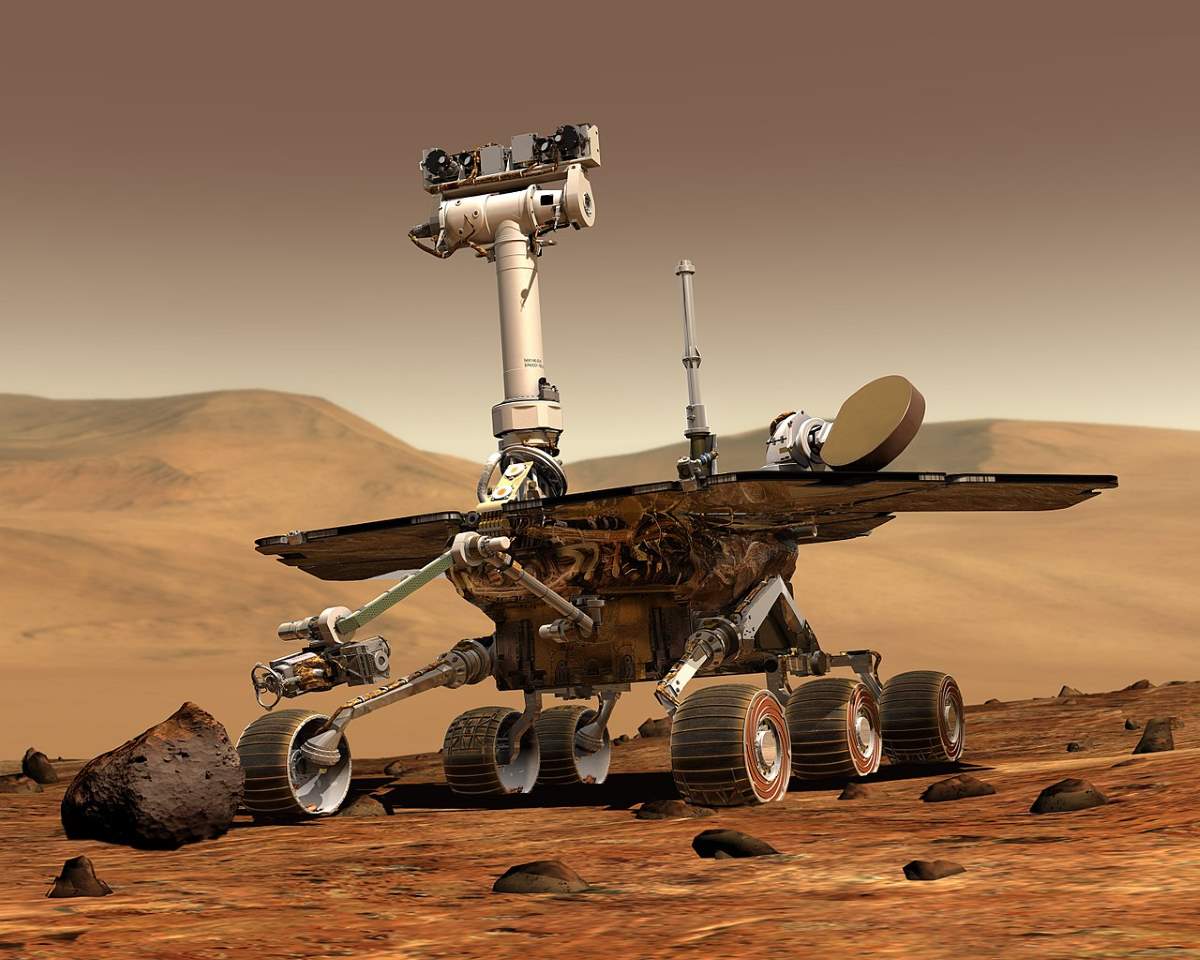
Opportunity landed on Mars on January 25, 2004
On January 15, 2004, NASA’s Opportunity rover landed on Mars (in Meridiani Planum), three weeks after its twin, Spirit, touched down on the other side of the red planet on January 4.
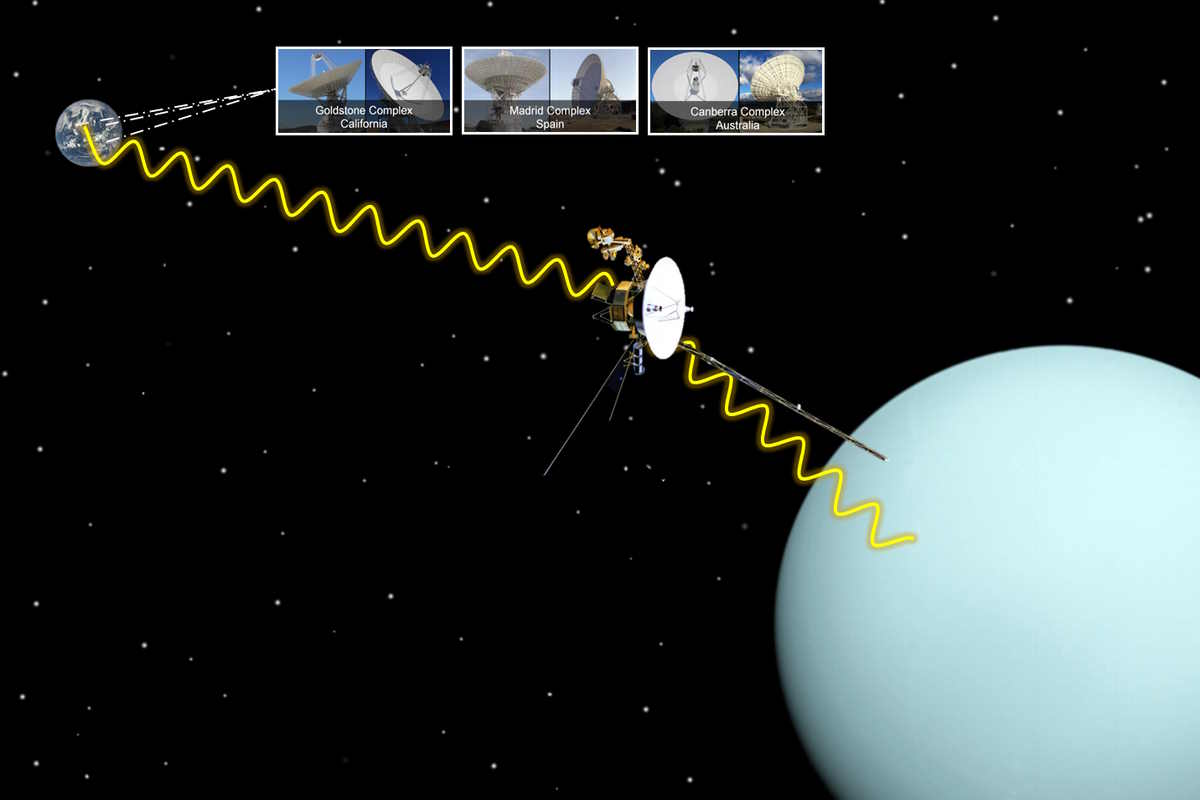
The first Uranus flyby was performed by Voyager 2 on January 24, 1986
On January 24, 1986, NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft performed the first (and as of 2023, the only so far) Uranus flyby in the history of space exploration.