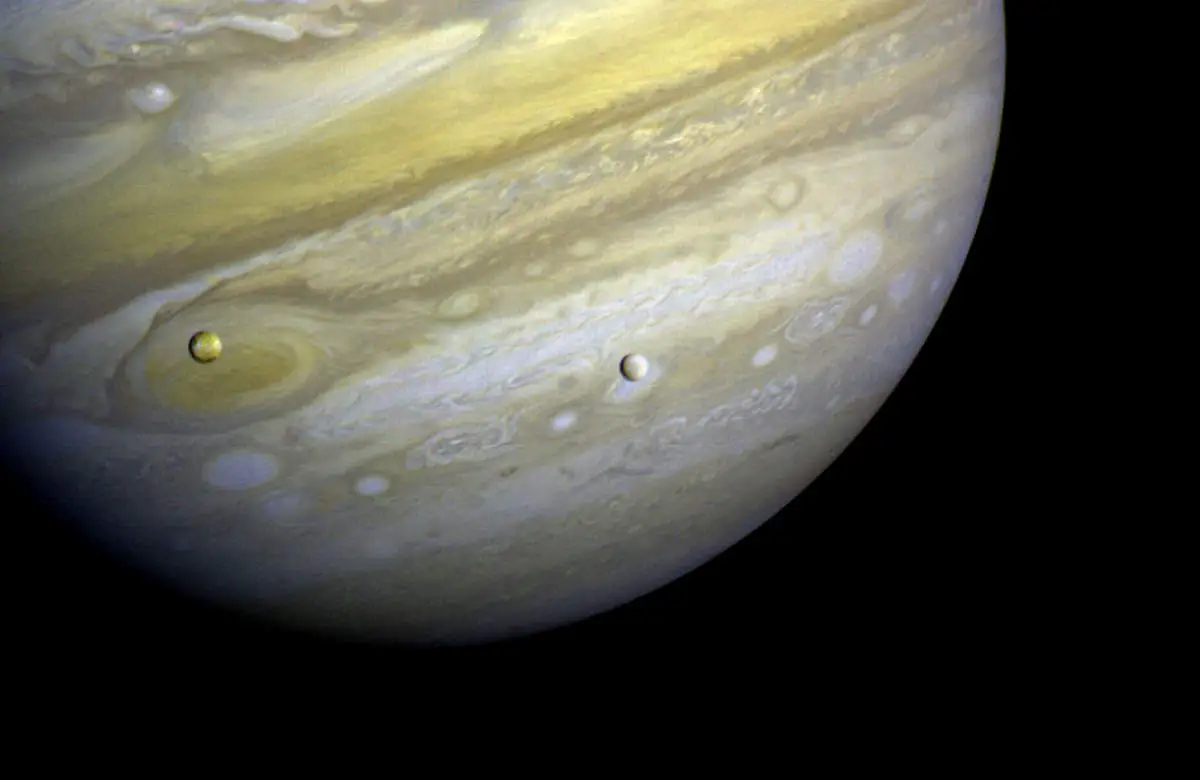
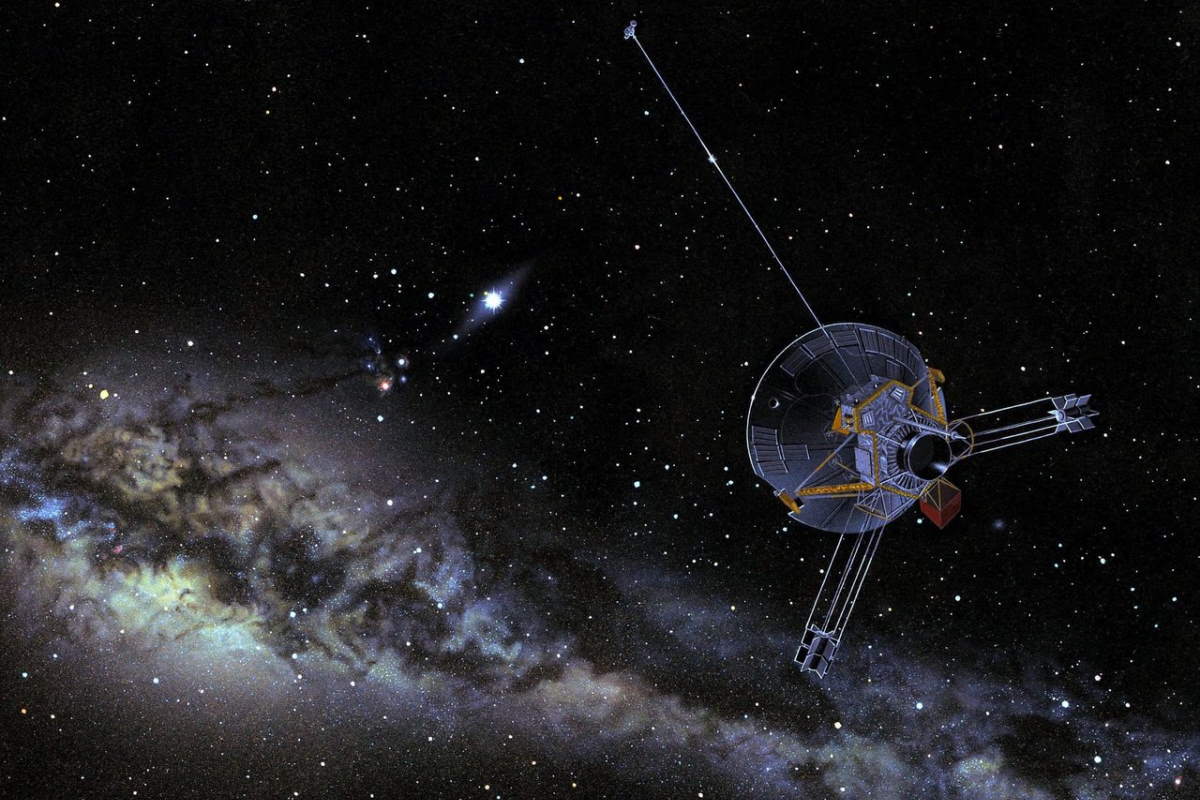
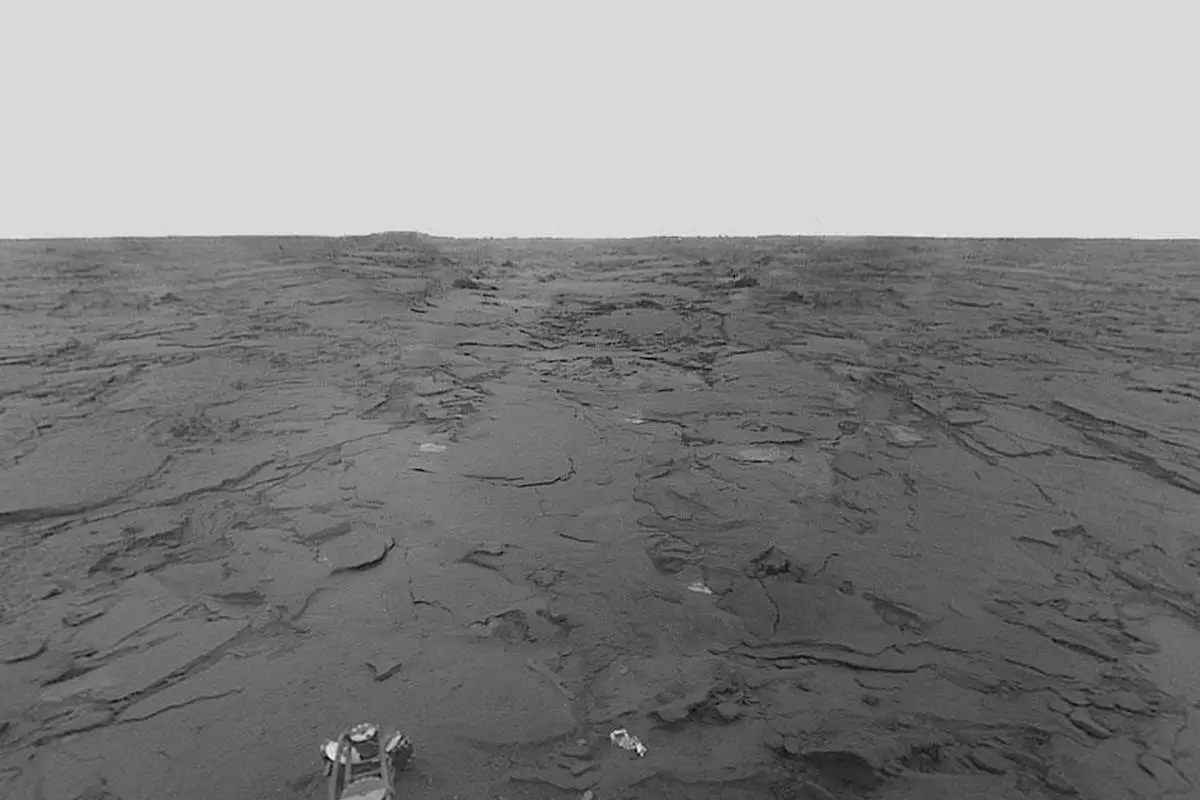
The budget of NASA from 1970 to 1979 marks a decade of transition and continued exploration in space science. Building on the success of the Moon landing, this period saw the development and execution of significant missions such as the Viking landings on Mars, the launch of Skylab, America’s first space station, and the inception of the Space Shuttle program. The funding during these years played a vital role in maintaining America’s leadership in space exploration and technology. In this article, we will examine the year-by-year budget of NASA that enabled these groundbreaking achievements and shaped the direction of human spaceflight and planetary exploration.






![Huygens spacecraft on Titan [artist concept]](https://cdn-0.ourplnt.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Huygens-spacecraft-on-Titan-artist-concept.jpg)
