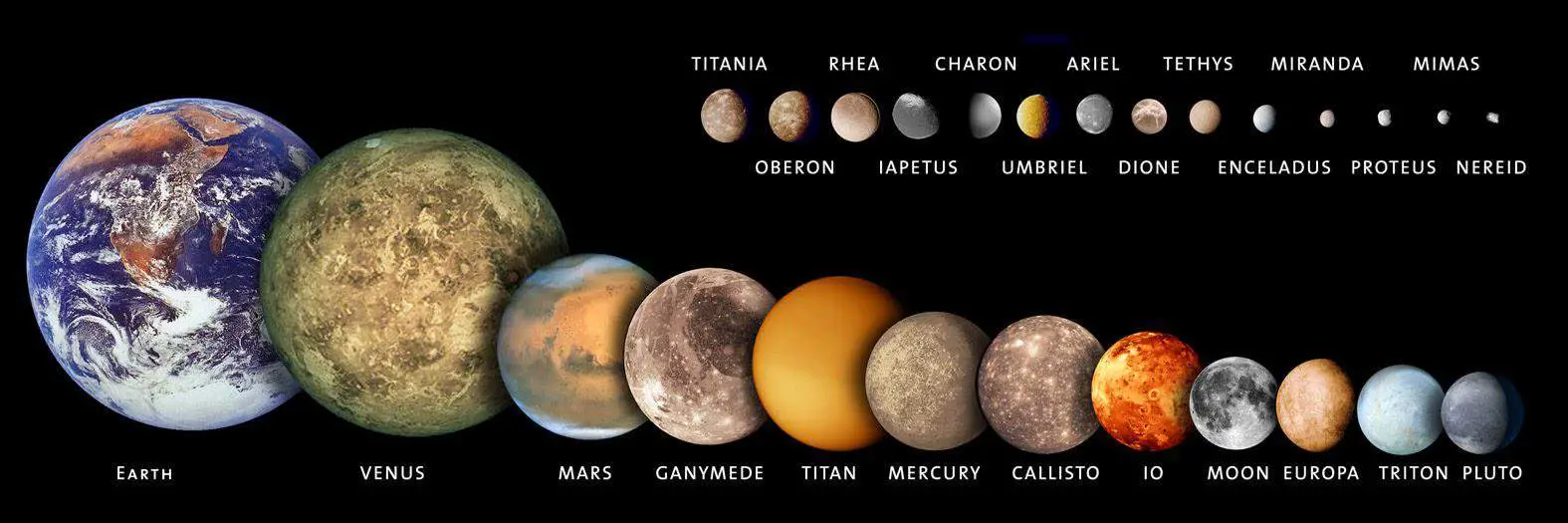
The Solar System is a vast and fascinating place that is home to a diverse range of celestial bodies, ranging from small asteroids to giant planets. However, there are also a number of objects that fall somewhere in between – they are not planets, but they are also not small enough to be considered asteroids or comets.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 largest non-planets in the Solar System. From massive moons to dwarf planets, these objects are fascinating in their own right and play an important role in our understanding of the cosmos. Let’s take a closer look at these intriguing objects and learn more about what makes them so unique.