On April 16, 1972, the huge, 363-feet (110.6 meters) tall Apollo 16 (Spacecraft 113/Lunar Module 11/Saturn V SA-511, see notes 1) space vehicle was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 12:54 p.m. EST. Crewed by Commander John W. Young, Lunar Module Pilot Charles Duke (see notes 2), and Command Module Pilot Ken Mattingly (see notes 3), it was the tenth crewed mission in the United States Apollo space program, the fifth and penultimate to land on the Moon and the first to land in the lunar highlands.
Today’s (April 16) story of what happened this day in Science, Technology, Astronomy, and Space Exploration history.
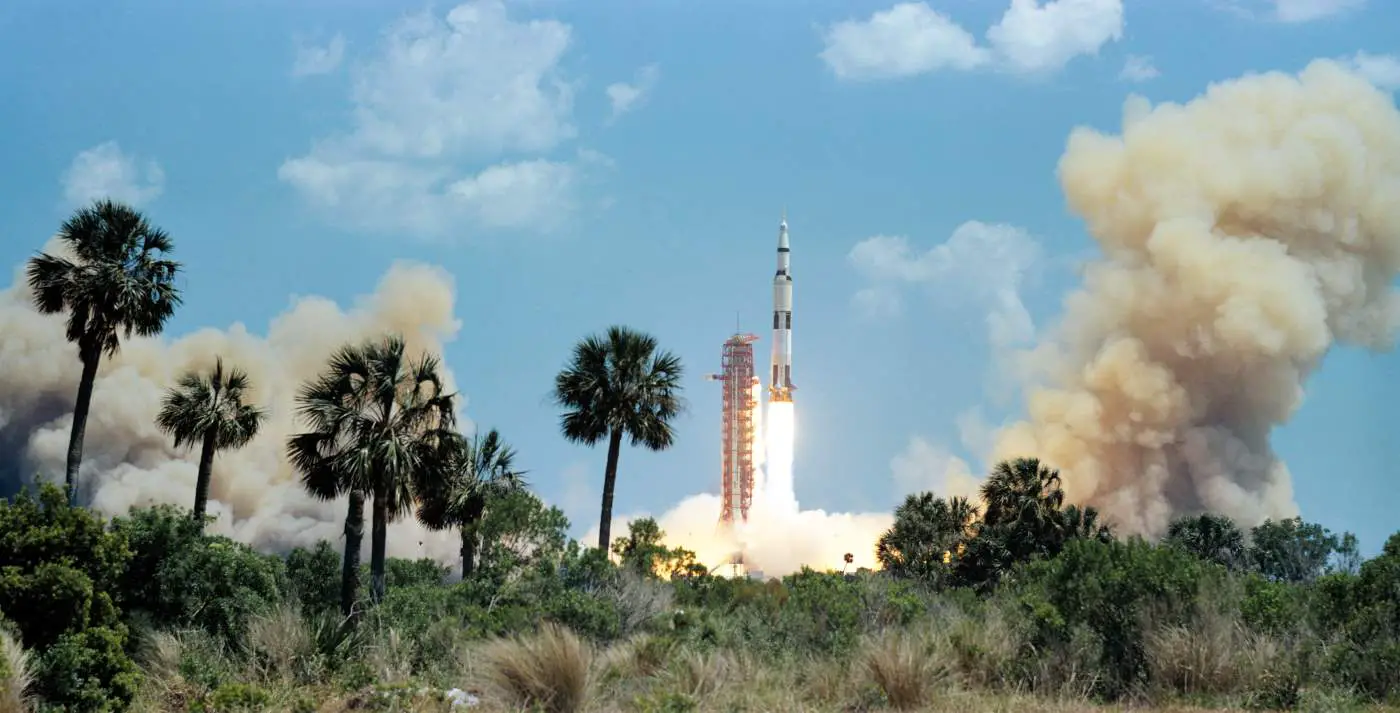

Video: Apollo 16 launch: Walter Cronkite and Walter Schirra LIVE on CBS, April 16, 1972. Synchronizing: Video images (80% similar to the CBS broadcast) come from “5V1NA70G YouTube channel” (NASA FEED), the sound is recorded on audio cassette to CBC (Radio Canada) from CBS TV Network. AUDIO Dan Beaumont archive. Dan Beaumont production.
Video: Apollo 16 launch with various launch pad cameras.
Related: Saturn V Rocket (Documentary)
Apollo 16
Apollo 16 was the second Type J mission (see notes 4), an extensive scientific investigation of the Moon from the lunar surface and from lunar orbit. Launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 12:54 PM EST on April 16, 1972, the mission lasted 11 days, 1 hour, and 51 minutes, and concluded at 2:45 PM EST on April 27.
The three crew members were Captain John Watts Young (USN), commander; Lt. Commander Thomas Kenneth “Ken” Mattingly, II (USN), command module pilot; and Lt. Colonel Charles Moss Duke, Jr. (USAF), lunar module pilot.
The primary objectives of the mission were:
- to perform selenological inspection, survey, and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Descartes region;
- to emplace and activate surface experiments; and
- to conduct in-flight experiments and photographic tasks.
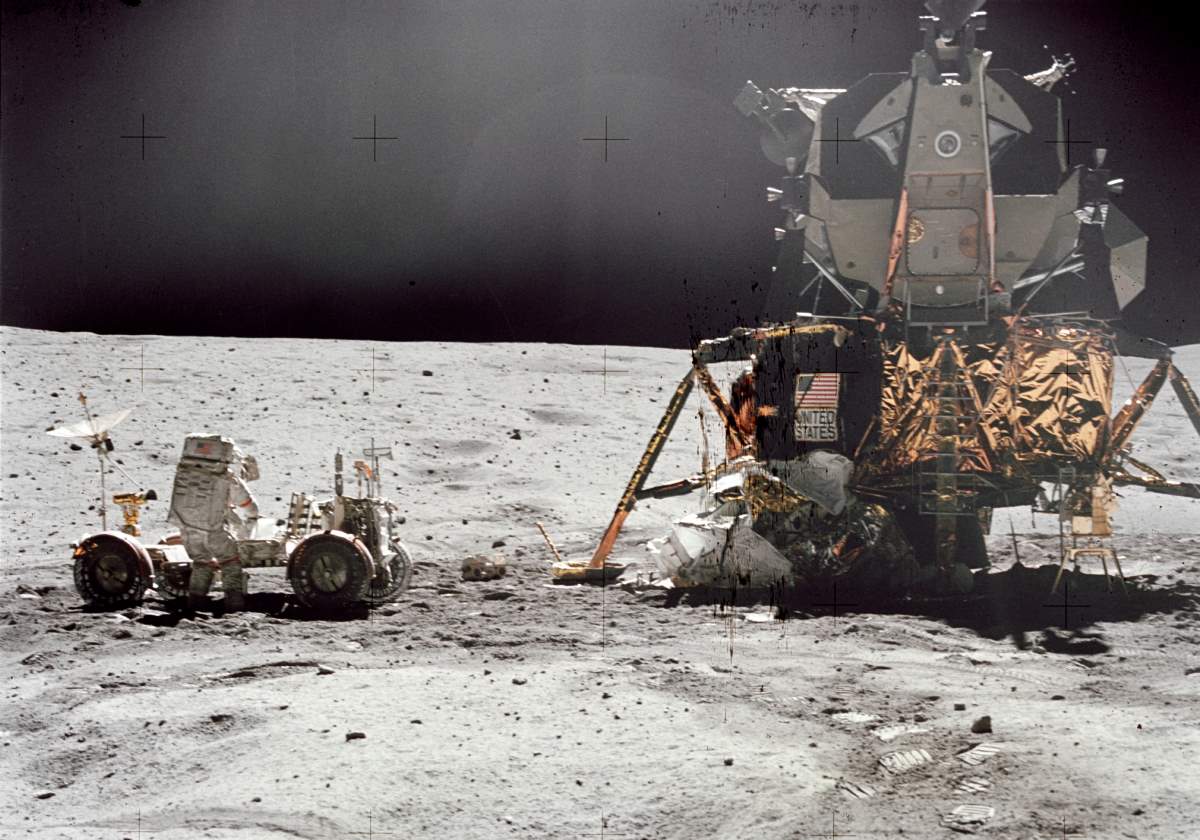
Young and Duke spent 71 hours -just under three days- on the lunar surface, during which they conducted three extra-vehicular activities or moonwalks, totaling 20 hours and 14 minutes. The pair drove the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), the second produced and used on the Moon, 26.7 kilometers (16.6 mi).
On the surface, Young and Duke collected 95.8 kilograms (211 lb) of lunar samples for return to Earth, while Command Module Pilot Ken Mattingly orbited in the Command/Service Module (CSM) above to perform observations. Mattingly spent 126 hours and 64 revolutions in lunar orbit. After Young and Duke rejoined Mattingly in lunar orbit, the crew released a subsatellite from the Service Module (SM). During the return trip to Earth, Mattingly performed a one-hour spacewalk to retrieve several film cassettes from the exterior of the Service Module.
Apollo 16’s landing spot in the highlands was chosen to allow the astronauts to gather geologically older lunar material than the samples obtained in the first four landings, which were in or near lunar maria. Samples from the Descartes Formation and the Cayley Formation disproved a hypothesis that the formations were volcanic in origin.

Notes
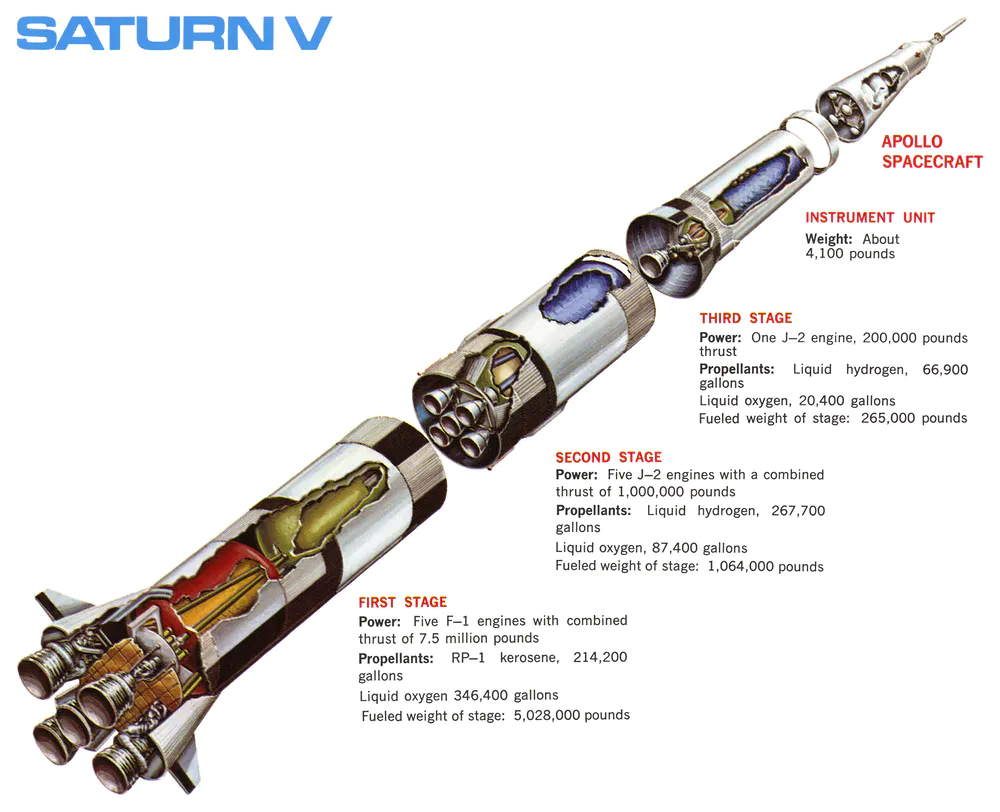
- The Saturn V was an American human-rated expendable rocket used by NASA between 1967 and 1973. With a thrust of 7.7 million lbs. (3.49 million kilograms), Saturn V is the most powerful rocket ever built. As of April 2018, the Saturn V remains the tallest, heaviest, and most powerful (highest total impulse) rocket ever brought to operational status, and holds records for the heaviest payload launched and largest payload capacity to LEO of 140,000 kg (310,000 lb). Saturn 5 is the rocket that took humanity to the Moon.
- Charles Moss “Charlie” Duke Jr. (born October 3, 1935), (Brig Gen, USAF, Ret.), is an American former astronaut, retired U.S. Air Force officer, and test pilot. As Lunar Module Pilot for Apollo 16 in 1972, he became the tenth and youngest person to walk on the Moon.
- Thomas Kenneth Mattingly II (March 17, 1936 – October 31, 2023), (RADM, USN, Ret.), better known as Ken Mattingly, was an American naval officer and aviator, aeronautical engineer, test pilot, Rear Admiral in the United States Navy, and astronaut who flew on the Apollo 16, STS-4 and STS-51-C missions.
- Type J mission: longer three-day stays using an Extended LM, with three LEVAs (Lunar Extravehicular Activity) and a Lunar Roving Vehicle (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, Apollo 17). Apollo 18 to 20 would have been J missions but they were canceled. Apollo 15 was originally planned as an H mission but was promoted to J as the program was curtailed.
Sources
- “Liftoff of Apollo 16” on NASA.gov
- Apollo 16 mission on NASA.gov
- Apollo 16 mission summary on history.NASA.gov
- Apollo 16 on Wikipedia
- Saturn V on Wikipedia
- Charles Duke on Wikipedia
- Ken Mattingly on Wikipedia
- List of Apollo mission types on Wikipedia
- Moon Landings: All-Time List [1966-2025] - February 2, 2025
- What Is Max-Q and Why Is It Important During Rocket Launches? - January 16, 2025
- Top 10 Tallest Rockets Ever Launched [2025 Update] - January 16, 2025
