Russian space agency Roscosmos started to publish declassified documents from the Space Race, a 20th-century arm-wrestling to achieve firsts in spaceflight capability between two Cold War rivals, the Soviet Union (USSR) and the United States (US).
Here is the announcement by Roscosmos:
“Roscosmos State Corporation continues publishing declassified documents dedicated to space exploration and crewed cosmonautics. Today we publish documents that will help reconstruct the first multiseat Voskhod spacecraft development details and its first flight.”
“55 years ago, on October 12, 1964, the Soviet Voskhod-1 spacecraft was launched from the launch pad No.1 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. The spacecraft crew included Commander Vladimir Komarov, research officer cosmonaut Konstantin Feoktistov and physician-cosmonaut Boris Yegorov. During the flight, the spacecraft made 16 circuits around the Earth with a flight distance of about 700,000 kilometers (435,000 miles). For the first time in the history of the nation’s spaceflights, the crew returned to Earth in a reentry vehicle.”
“After the Voskhod-1 multiseat flight another task was set – to perform the first extravehicular activity. A few months later, on March 18, 1965, another spacecraft of the same type was launched from Baikonur. This time the crew included two cosmonauts: Pavel Belyaev and Alexey Leonov. This mission was the first-ever human spacewalking activity. Leonov’s extravehicular activity lasted 23 minutes and 41 seconds with 12 minutes and 9 seconds outside the spacecraft itself.”

“Voskhod-type spacecraft was substantially different from Vostok spacecraft, its predecessors. Besides the three-seat cabin, Voskhod vehicles featured new equipment and revolutionary systems. For the first time, the cosmonauts performed a spaceflight without spacesuits and ejection systems. The spacecraft was equipped with a soft landing system and marked the beginning of a new stage in direct space exploration by humans.”
“Roscosmos State Corporation expresses gratitude to the state archives: Russian State Archive of Contemporary History and personally to its Director Natalya Tomilina, Russian State Archive for Scientific-Technical Documentation and its director Marina Vlasova, as well as to RSC Energia and TsNIIMash for the documents provided.”
You can access today’s published declassified documents on the Roscosmos website (the website is in Russian but the auto-translate works well).
Published Document examples by Roscosmos
October 12, 1964: “RISE” at the dawn of the space age – the first multi-seat ship

The first Soviet cosmonauts, Yuri A. Gagarin, G. S. Titov, A. G. Nikolaev, P. R. Popovich, V. F. Bykovsky, and V. V. Tereshkova, flying in 1961-63 on the single-seat spaceships “Vostok”, they carried out an extensive program of scientific, technical, and biomedical research in orbit.
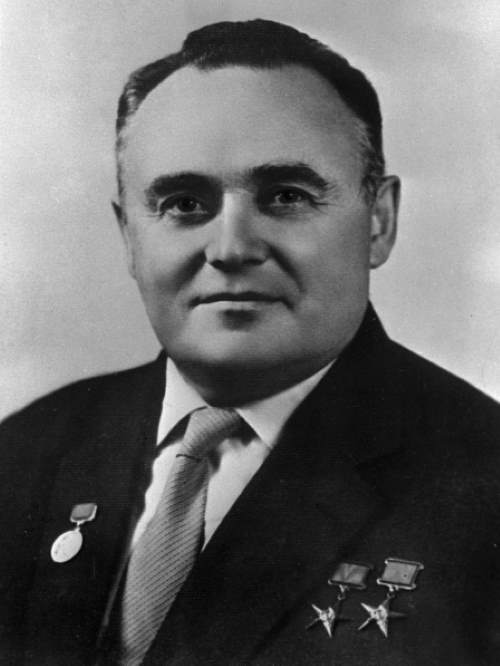
However, the expansion of the range of scientific tasks and the logic of the further development of manned space exploration dictated the need for further improvement of spacecraft and the creation of more complex lunar and interplanetary spacecraft. To solve the problems of docking and orbital assembly, OKB-1, under the guidance of SP Korolev, designed the first Soyuz space complex.
Simultaneously with a great lead in the United States, Gemini two-seater spaceships (Gemini) were being developed. In order not to lag behind, SP Korolev proposed modifying the Vostok ship, whose systems have demonstrated their reliability.
The preliminary design of the ship, in which three people could work during the day, was called “Sunrise” and was approved on February 12, 1964. And already on October 12 of the same year, a crew consisting of pilot-cosmonaut V.M. Komarova (commander of the ship), scientist K.P. Feoktistov and doctor BB Egorova.
The manned flight of the American two-seater “Gemini” took place almost six months later – on March 23, 1965.
Multi-seat spacecraft “Voskhod” (English: Sunrise)
A document signed by the chief designer of OKB-1 S.P. Korolev on February 12, 1964, indicates that on the basis of the single-seat spacecraft “Vostok” can be created multi-seat ship “Sunrise” while maintaining the basic concept and circuit design of the original product.
“To ensure the flight of three people in the Voskhod ship, it is necessary (in comparison with the Vostok ships) to reconfigure the equipment in the descent vehicle, install three pilot seats, having removed the ejection seat and spacesuit, modify a number of on-board systems and install additional equipment “.
Album of drawings and illustrations for the technical description and operating instructions for the display, alarm and manual control system SIS-3-3KV of the Voskhod spacecraft
Photos, descriptions, and operation diagrams of indicator devices and controls in the cockpit of the Voskhod ship designed for OKB-1 at the Special Design Bureau of the Flight Research Institute (SKB LII) under the supervision of Chief Designer S. G. Darevsky.
Letters S. P. Korolev about the need for system improvements for the Voskhod ship
Letters sent by Sergei Pavlovich Korolev February 2, 1964, to the heads of the enterprises of cooperation, as well as to the General Staff of the Navy with a request for the necessary modifications of communication systems, telemetry transmission, and search for Vostok ships for use on Voskhod ships, taking into account the fact that Voskhod flights “It is supposed to be held in June-July of this [1964].”

The private work program of the astronaut – research assistant in flight on the Voskhod-3KV spacecraft
The document, approved by the chief designer of OKB-1 academician S. P. Korolev on June 9, 1964, defines the special tasks, contents, and schedule of the work of the astronaut – a scientific employee, as one of the members of the Voskhod crew. It is emphasized that the general tasks (the duty of the watch, medical experiments, and tests, etc.) are determined by the “flight mission of the crew of the ship.”
The protocol of the meeting of the technical management on the facilities “3KV” and “3KD” dated July 8, 1964
Document signed by S. P. Korolev contains reports of responsible executives on the preparation of trials of the 3KV (triple ship Voskhod) and 3KD (double ship Vykhod – Voskhod 2) and the main milestones, and also contains an exchange of views, during which the main OKB-1 designer answers questions of responsible executors of works. Among other things, S.P. Korolev notes: “I think, to solve the issue of [on-board] film and photography of astronauts … it is necessary to attract specialized institutions and highly qualified specialists.”
Decree of the Council of Ministers of the USSR “On the launch of the Voskhod spacecraft”
The document, signed on August 19, 1964, approves the proposal to launch “in August-September 1964 the launch of one or two Voskhod ships with mannequins for testing the systems and equipment of ships and carriers, and in September-October – the manned … Voskhod spacecraft with three astronauts on board, ” and also entrusts the leadership of the preparation and launches with a commission whose composition is specified in the document. A draft TASS message on the launch of the Voskhod manned spacecraft with the attached text is also approved.
The logbook of the spacecraft Voskhod “Sunrise” 1964
The commander of the world’s first three-seater ship “Voskhod” V.M. Komarov controlled the spacecraft, conducted radio communication sessions with the Earth, controlled the stages of flight and the operation of onboard systems, and led the actions of crew members.
By changing the handwriting in the logbook, it is clearly visible which entries were made before and which were made during the flight. For developers, comments on the ease of use of cab systems were especially valuable.
During the flight, the researcher (in modern terminology – flight engineer) of the Voskhod ship K.P. Feoktistov monitored the execution of the flight mission, constantly observing various points related to the operation of the ship’s systems and the execution of various experiments, “carried out photographing and filming of space, ground objects, auroras, horizon lines, and luminous particles through the porthole, trying to identify the characteristics of objects shooting.”
The journal of the physician of the spacecraft Voskhod 1964
Doctor B.B. Egorov in flight took blood samples from the crew, measured blood pressure, conducted medical self-monitoring, biological experiments, and tests. He wrote: “10:45 … Everyone has mild hyperhidrosis. They included a dehumidifier. After the first minutes of acclimatization, they zealously set to work. Everyone is trying to move as smoothly as possible … “
Report on the results of the experimental development of the head fairing discharge system
Document signed by S.P. Korolev July 31, 1965, summarizes the result of experimental testing of the discharge of the head fairing of the launch vehicle of the Voskhod vehicle at the ground stand. It is noted that “the methodology for preparing and conducting tests, the composition of the experimental setup allows … to obtain during the experiment, the necessary data on which … you can judge the operation of the test system in flight conditions …”
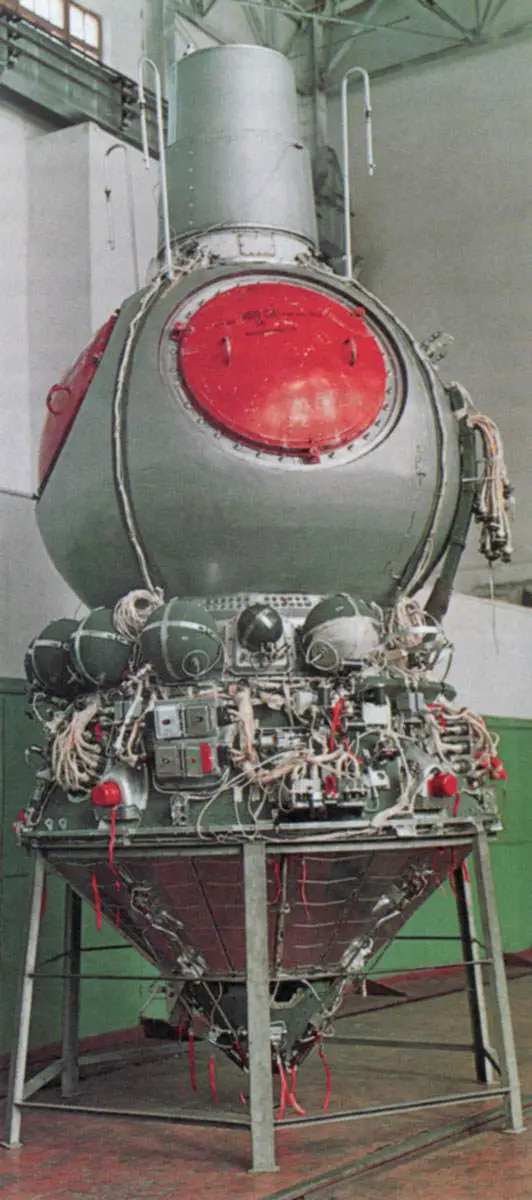
Voskhod 1
The world’s first multi-seat spaceship Voskhod was launched into orbit on October 12, 1964.
The crew included the commander – Colonel Engineer Vladimir Mikhaylovich Komarov, research scientist-cosmonaut – Konstantin Petrovich Feoktistov, and cosmonaut – Boris Borisovich Yegorov.
During the day in space, the ship circled the globe 16 times and, having completed the flight program, successfully landed on Soviet territory.
In the conditions of a daily space flight, a new multi-seat manned spacecraft was tested, extensive biomedical research was performed, the working capacity and interaction of specialized astronauts in various fields of science and technology were checked, scientific physical and technical studies were carried out, the study of the influence of various space flight factors was continued. on the human body.
The Voskhod crew set four world records in its class:
- maximum space flight altitude (408 km – 53 mi);
- maximum mass (5,320 kg – 11,729 lbs) raised to such a height;
- range (669,784.027 km – 416,184 mi);
- flight duration (24 hours 17 minutes 03 seconds).
The flight of Voskhod marked the beginning of a new stage in the development of space technology: multi-seat ships made it possible to complicate the targets of flights and perform complex scientific, technical, and biomedical research.
Sources
- Space Race on Wikipedia
- Voskhod 1 on Wikipedia
- Sergei Korolev on Wikipedia
- Roscosmos website
- Roscosmos on Wikipedia
- Budget of NASA, Year by Year [1980-1989] - June 10, 2024
- Budget of NASA, Year by Year [1970-1979] - June 10, 2024
- Budget of NASA, Year by Year [1958-2024] - June 10, 2024

