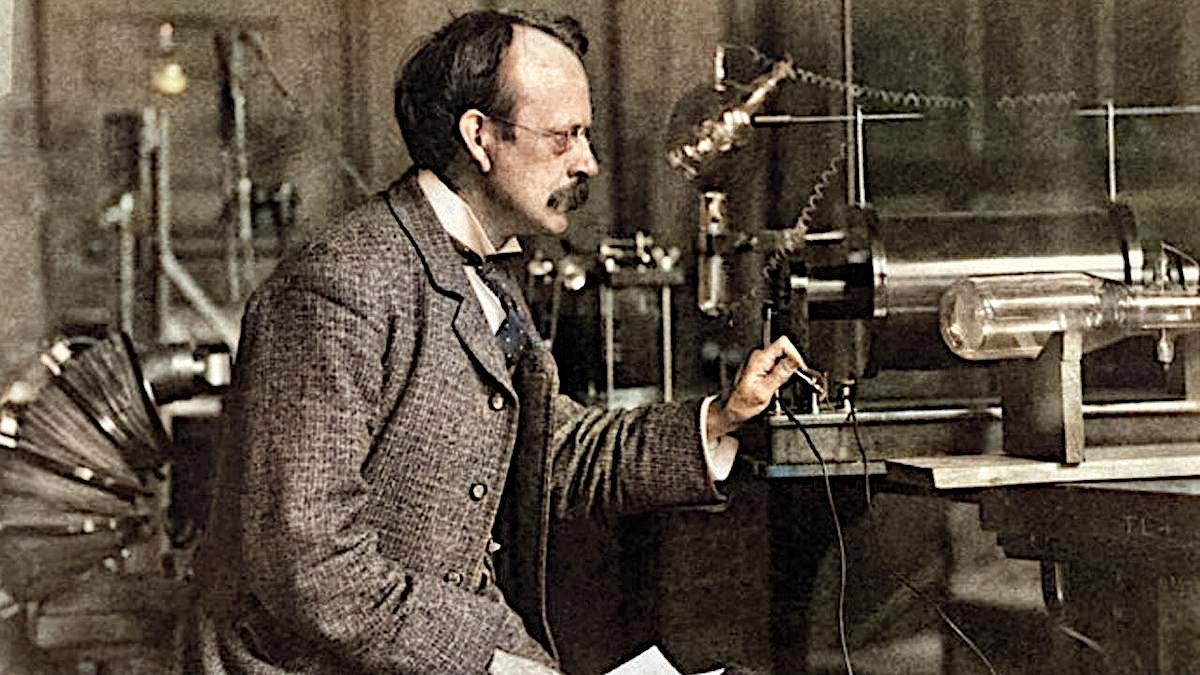On April 30, 1897, British physicist and Nobel Laureate in Physics, Sir Joseph John Thomson (commonly known as J. J. Thompson, 18 December 1856 – 30 August 1940) announced the existence of electrons.
Thompson called the particles “corpuscles”, meaning “small bodies”, but later scientific community preferred the name electron which had been suggested by the Irish physicist George Johnstone Stoney in 1891 because these particles are the fundamental unit of electricity (see notes 1).
The word electron is a combination of the words electric and ion (a suffix, appearing in words of Latin origin, denoting action or condition). The suffix -on which is now used to designate other subatomic particles, such as a proton or neutron, is in turn derived from electron.